Investigation / Analysis / Study
CAE (Computer Aided Engineering)
Computer Aided Engineering is In design and development process, estimate and evaluate function and performance of the designed products by numerical analysis, using the computer simulation.
Analysis Example: Analysis of stress for hose clip
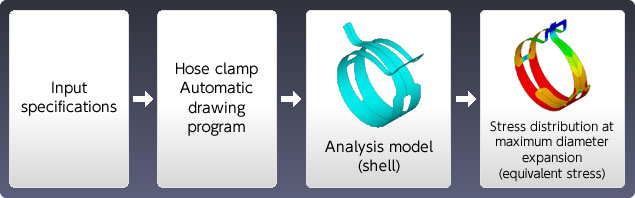
Benefits of Analysis
- Optimal adjustment of developed shape (dispersion of stress concentration)
- Optimal adjustment of pinch angle (improves drawability of holder)
- Optimal adjustment of maximum diameter (easier assembly)
Investigation / Analysis
1. Non-Contact Optics Type 3D Digitizer (ATOS)
Generates a 3D image of parts through non-contact imaging. Conducts comparison of actual dimensions and drawing values (design values).
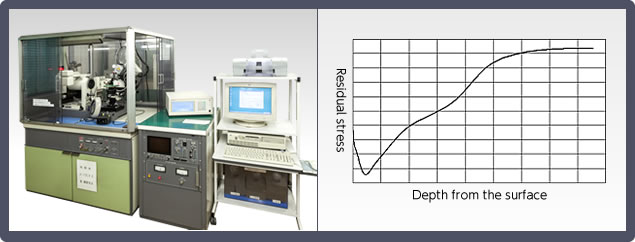
2. X-Ray Residual Stress Measurement
Uses X-ray diffraction phenomenon to check the residual stress.
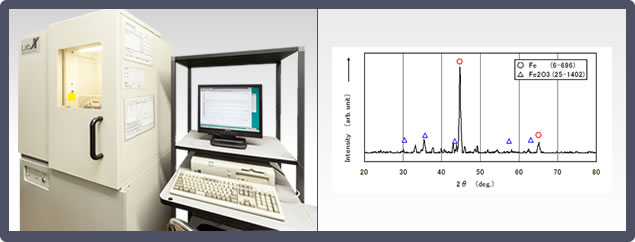
3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
Uses X-ray diffraction phenomenon to check the crystalline structure of substance.
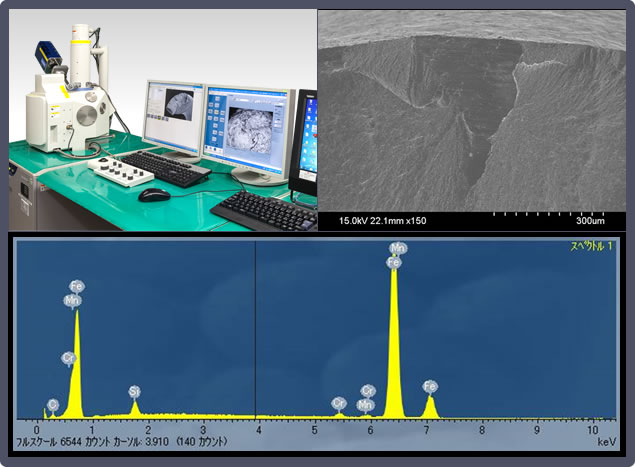
4. Scanning Electron Microscope / Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectrometry (SEM/EDX)
Uses electron beam irradiation to perform fracture analysis and enlarged observation, as well as to check constituent elements.
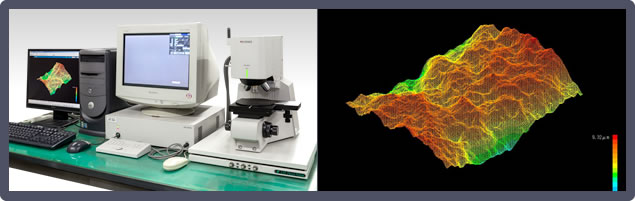
5. Laser Microscope
Uses a laser to measure the shape and roughness of a sample surface.
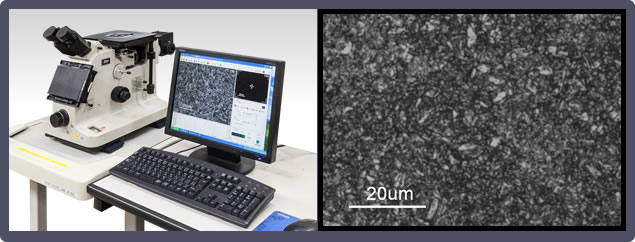
6. Metallograph
For observing the metallographic structure of a sample.
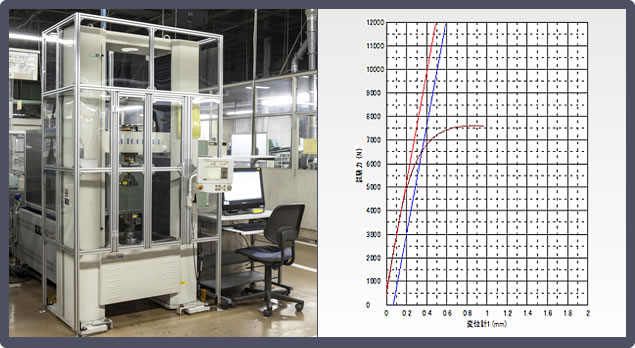
7. Universal Testing Machine
For checking the tension and compression strength of a sample.
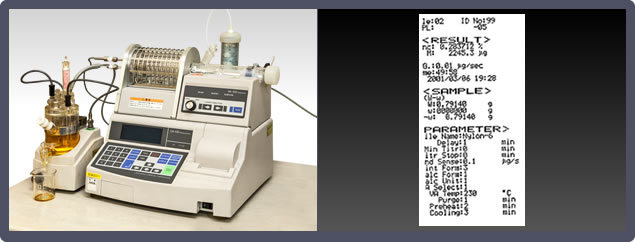
8. Trace Water-Content Measuring Instruments
Uses the Karl-Fischer Method to check trace water content.
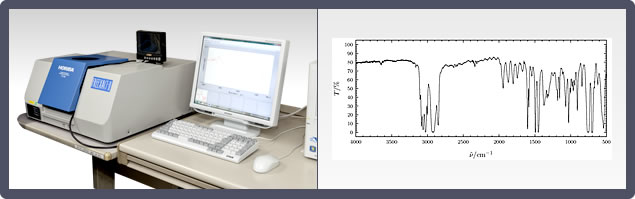
9. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer (FT-IR)
Uses irradiation of infrared rays to check the properties of a sample.
3D Printer
Based on 3D CAD data, creates a three-dimensional model by layering cross-sectional shapes.
Increases development speed and reduces cost.




